Department of Civil Engineering

VISION
MISSION
2. To develop innovation and research traits in students through frequent interaction with people from the industry, research centres, internships, site visits and state-of-the-art laboratories.
3. To impart environmental awareness programs to educate society and instil values to develop a sustainable, eco-friendly world.
VISION
2. To develop innovation and research traits in students through frequent interaction with people from the industry, research centres, internships, site visits and state-of-the-art laboratories.
3. To impart environmental awareness programs to educate society and instil values to develop a sustainable, eco-friendly world.
PROGRAM OUTCOMES (POs)
1. Engineering Knowledge
Apply the knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering fundamentals, and an engineering specialisation to the solution of complex engineering problems.

2. Problem analysis
Identify, formulate, research literature, and analyse complex engineering problems reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of mathematics, natural sciences, and engineering sciences.

3. Design/ Development of Solutions
Design solutions for complex engineering problems and design system components or processes that meet specified needs with appropriate consideration for public health and safety, cultural, societal and environmental considerations.

4. Conduct investigations of complex problems
Use research-based knowledge and research methods including design of experiments, analysis and interpretation of data, and synthesis of the information to provide valid conclusions.
5. Modern Tool Usage
Create, select, and apply appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering and IT tools including prediction and modelling to complex engineering activities with an understanding of the limitations.

6. The Engineer and Society
Apply reasoning informed by the contextual knowledge to assess societal, health, safety, legal, and cultural issues and the consequent responsibilities relevant to the professional engineering practice.

7. Environment and Sustainability:
Understand the impact of the professional engineering solutions in societal and environmental contexts, and demonstrate the knowledge of need for sustainable development.

8. Ethics
Apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of the engineering practice.

9. Individual and Team Work
Function effectively as an individual, and as a member or leader in diverse teams, and in multidisciplinary settings.
10. Communication
Communicate effectively on complex engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large, such as, being able to comprehend and write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations, and give and receive clear instructions

11. Project Management and Finance
Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the engineering and management principles and apply these to one’s own work, as a member and leader in a team, to manage projects and in multidisciplinary environments.

12. Life-long learning
Recognise the need for, and have the preparation and ability to engage in independent and life-long learning in the broadest context of technological change.
Program Specific Outcomes (PSOs):
1. To create structures with optimal design by using knowledge of strength of materials and codal provisions
2. To develop alternate building materials by using industrial waste and C & D waste, strength is checked by experimental results and simulated by software. Learn to use BIM for efficient project management.
3. To implement effective solid waste management, rain water harvesting by the knowledge of environmental engineering and to develop ground improvement technique by the knowledge of geotechnical engineering.
COURSE OUTCOMES (COs)
Bachelor of Engineering
2022 Scheme
Civil Engineering
2021 Scheme
Civil Engineering
2018 Scheme
Civil Engineering

Our Faculty

Dr. Altamashuddin Khan Nadeemallah
Teaching exp. 7 years,
Industry exp. 1 year.
Research exp. 4 years.

Dr. Purushothama C T
Teaching exp. 34 years.
Research exp. 7 years.

Prof. Zaheer Ahmed
Teaching exp. 13 years.
Research exp. 3 years.

Mr. Badruddin P M
Teaching exp. 15 years.
Industrial exp. 5 years.

Dr. Pooja K

Mr. Anjan Kumar MU
Teaching exp. 7 years.

Thejaswini K.L
Teaching experience - 6 years

Prasanna Prakash
Teaching experience - 6 years
Technical Staff

Mr. Ahmed shaifu

Mr. Nagaraj Budihal
1. Building Materials Testing Laboratory
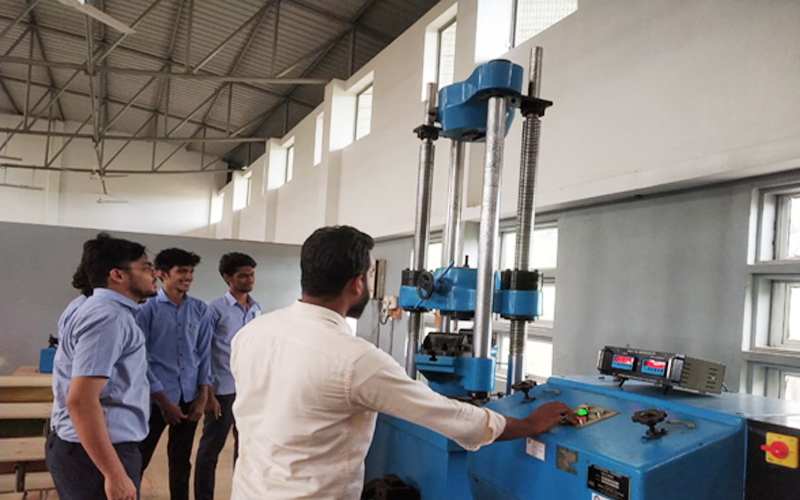
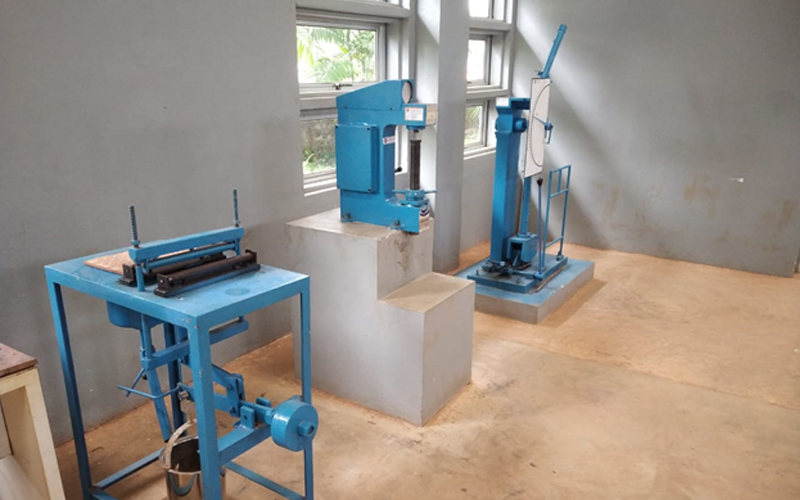



A Building Materials Testing Laboratory is a facility that tests construction materials for quality, strength, durability, and other properties to ensure they meet the required building codes and standards
2. Engineering Geology Laboratory
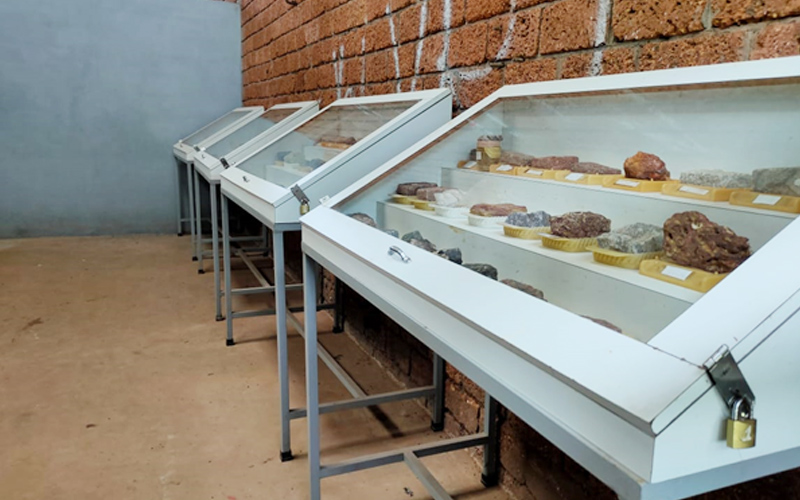
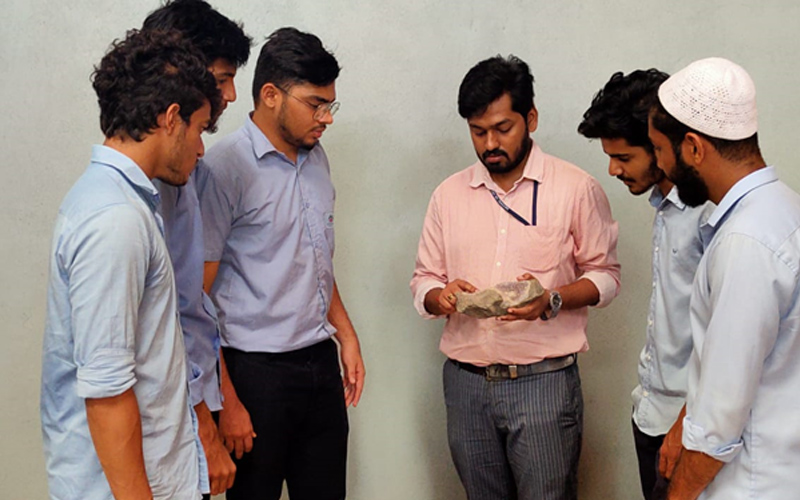
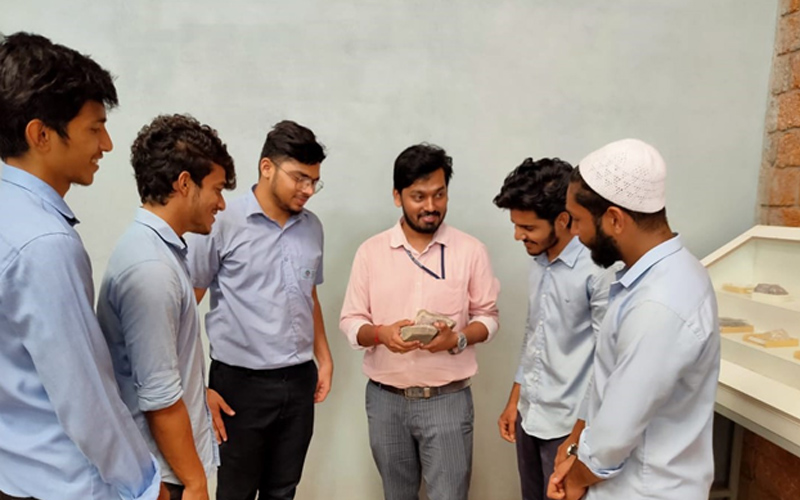



An Engineering Geology Laboratory is a facility that studies the physical and chemical properties of rocks, soils, and other geological materials to determine their suitability for construction and engineering projects. It focuses on evaluating geological materials for their strength, stability, and deformation properties, as well as their response to environmental factors like water, temperature, and pressure. The laboratory also studies geological hazards like landslides, earthquakes, and rockfalls, and provides recommendations to engineers and architects on how to mitigate the risks associated with these hazards.
3. Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines Laboratory
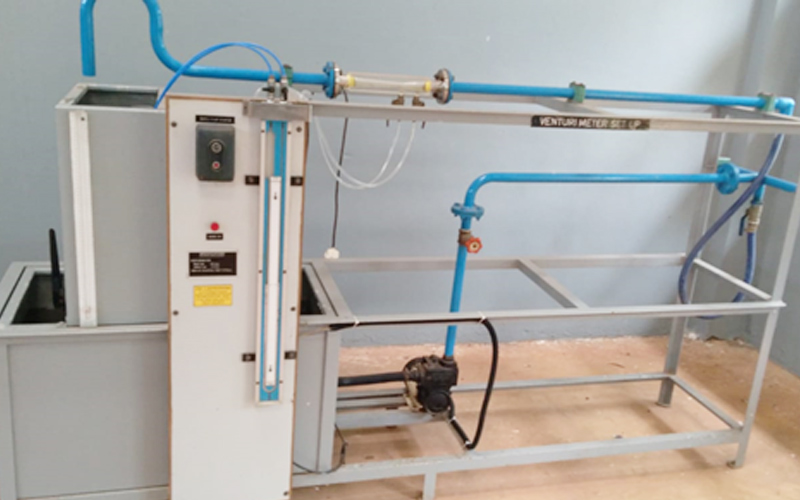
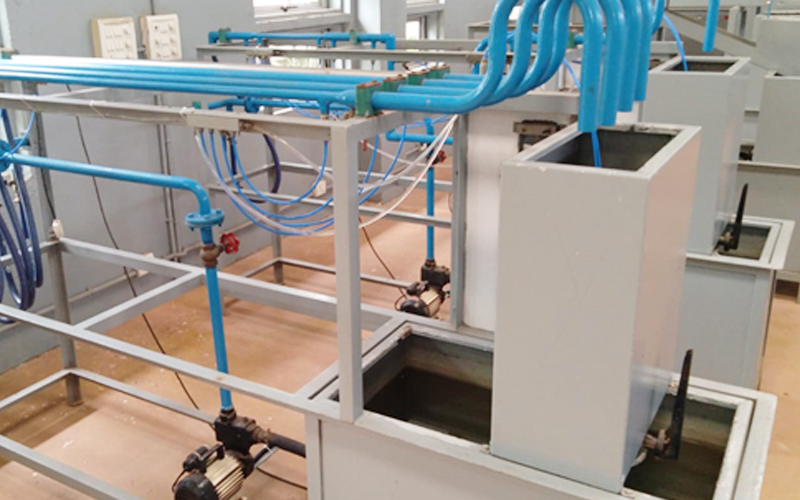
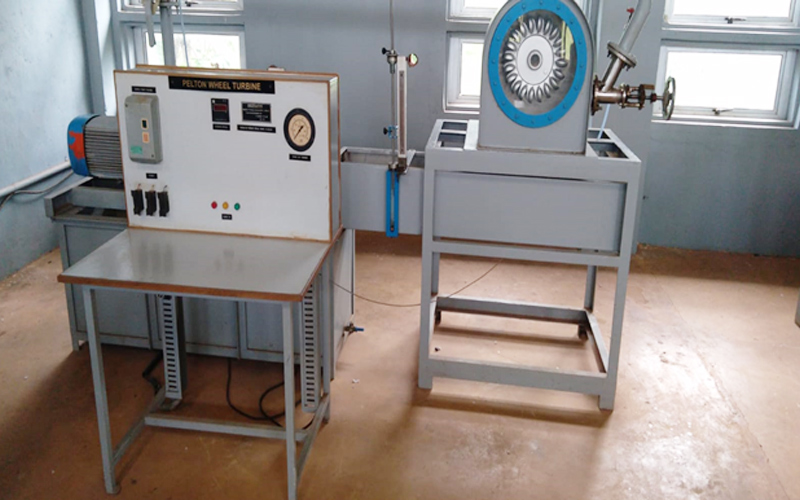
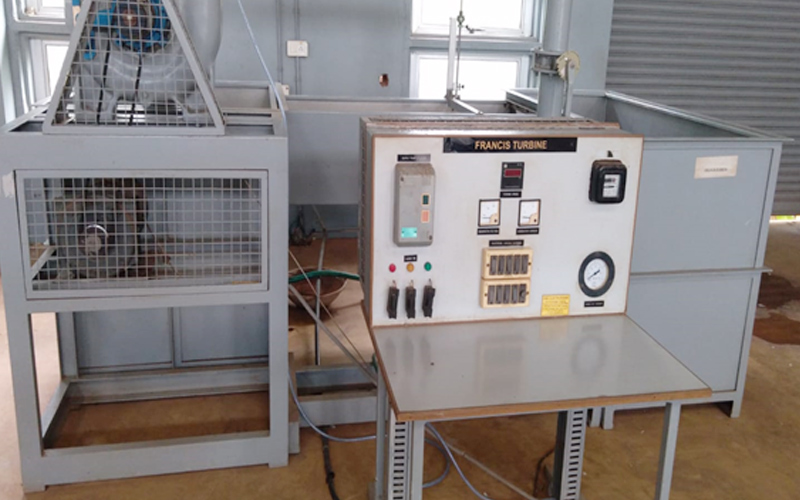




A Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines Laboratory is a facility that studies the behavior of fluids (liquids and gases) and their interaction with solid objects. The laboratory uses equipment such as flow meters, pressure gauges, and hydraulic machines to measure fluid properties like velocity, pressure, and flow rate. It also studies the principles of hydraulic machines such as pumps, turbines, and hydraulic systems used in engineering applications. The laboratory provides students and researchers with hands-on experience in fluid mechanics and hydraulic engineering, enabling them to design and analyze fluid systems used in various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and energy.
4. Surveying Laboratory
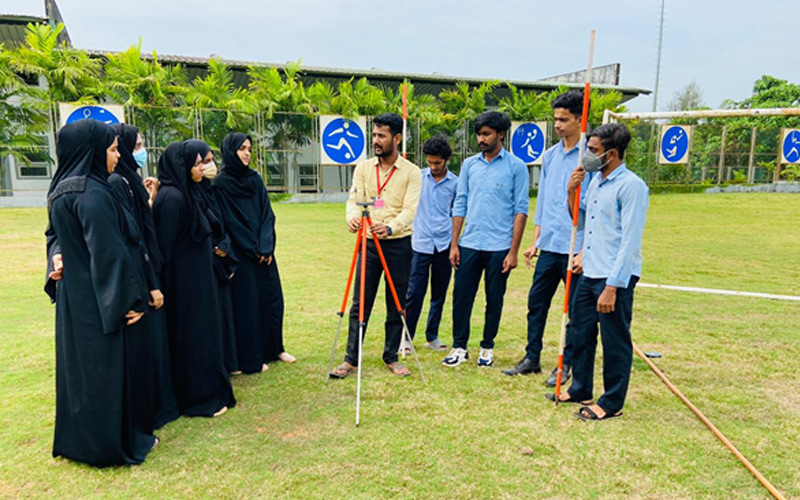
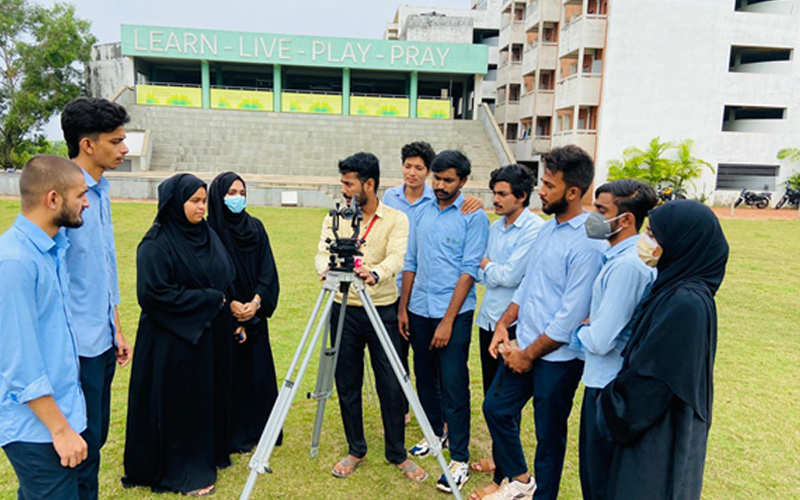
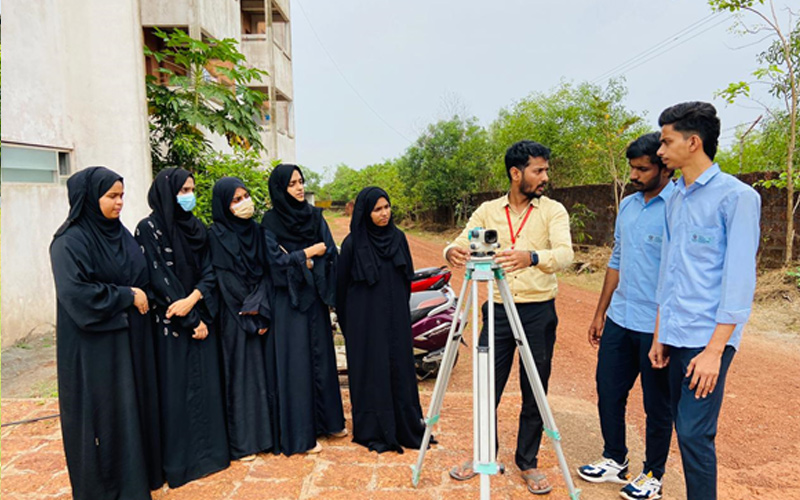



A Surveying Laboratory is a facility equipped with advanced instruments and software used for teaching and research in land surveying, measurement, and mapping. It provides hands-on training to students and researchers and offers services such as land surveying and mapping for engineering and construction projects.
5. Concrete and Highway Materials Laboratory
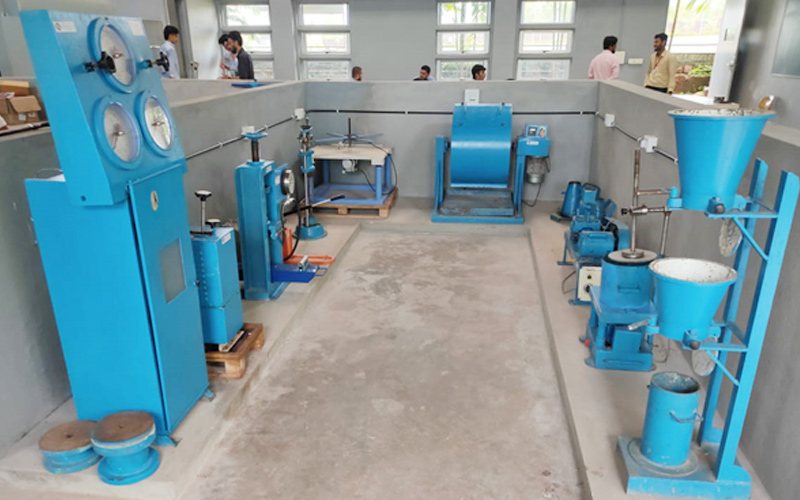
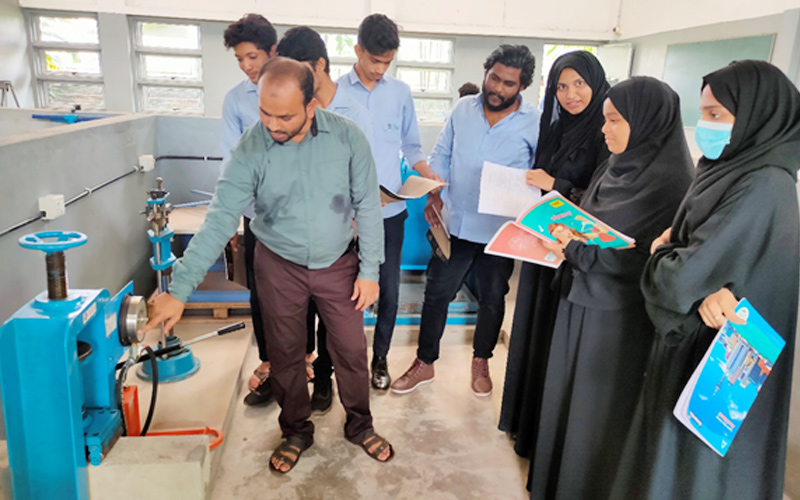
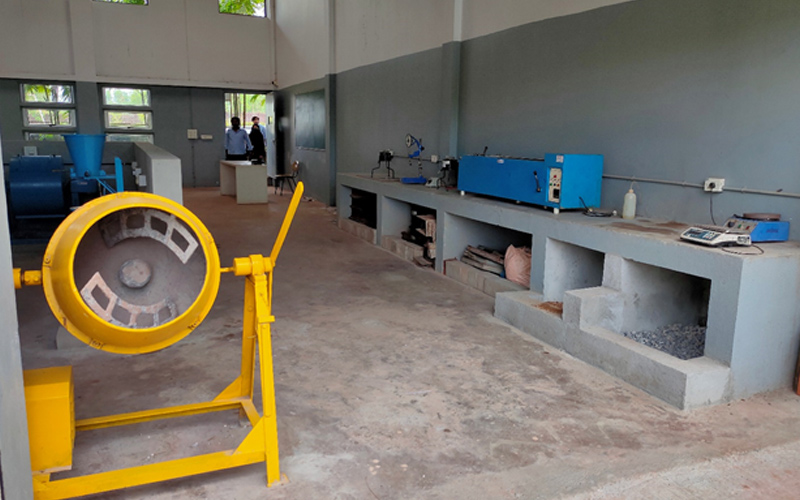



A Concrete and Highway Materials Laboratory is a facility that tests construction materials such as concrete, asphalt, and aggregates used in highway and transportation infrastructure projects. It evaluates their physical and mechanical properties to ensure safety, durability, and sustainability requirements are met.
6. Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory
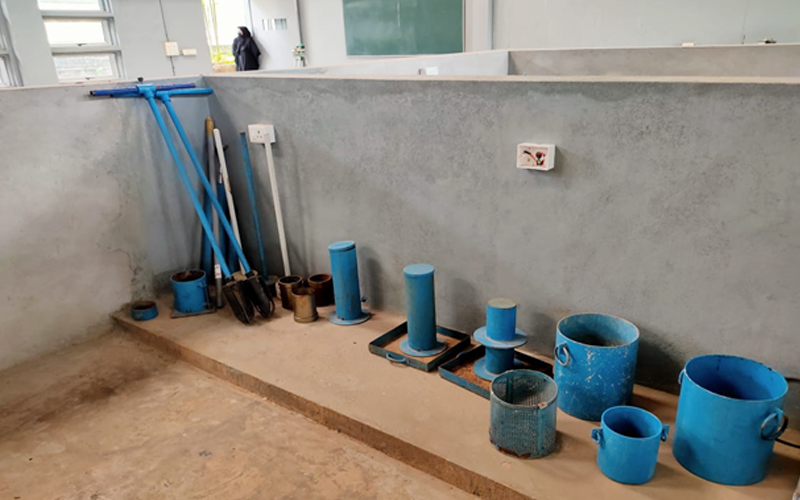
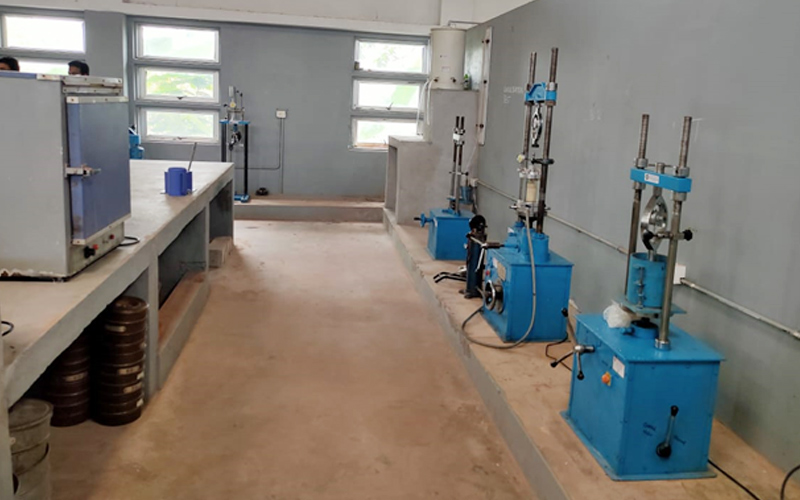
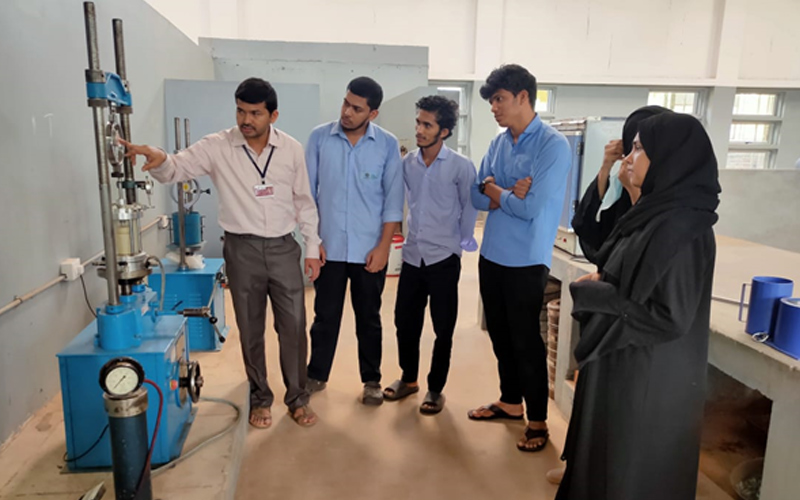



A Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory is a facility that studies the properties of soil and rock samples to evaluate their behavior under different conditions. It provides valuable data for designing and constructing safe and sustainable civil infrastructure projects, such as foundations, retaining walls, and tunnels.
7. CADD Lab
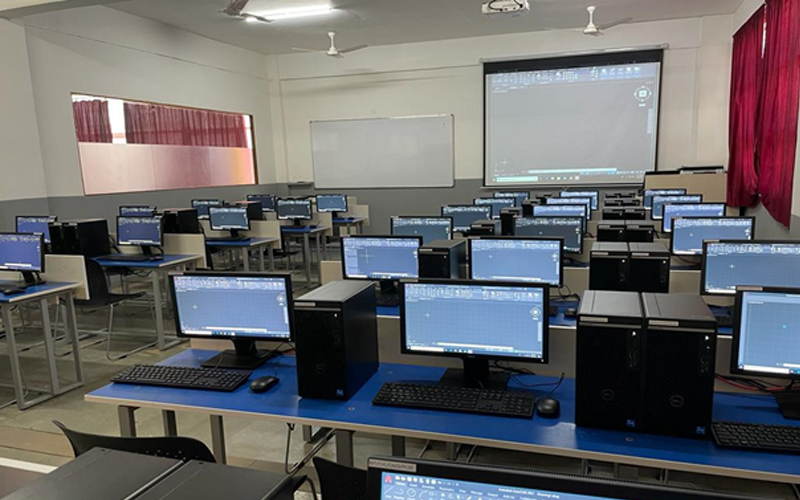
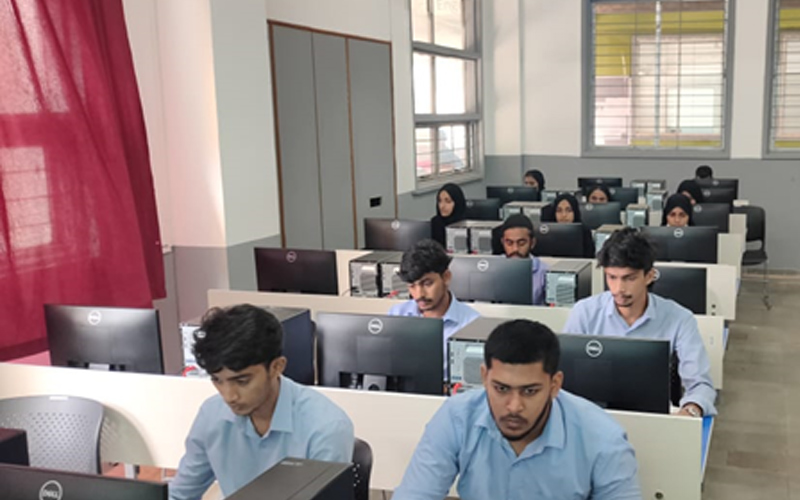
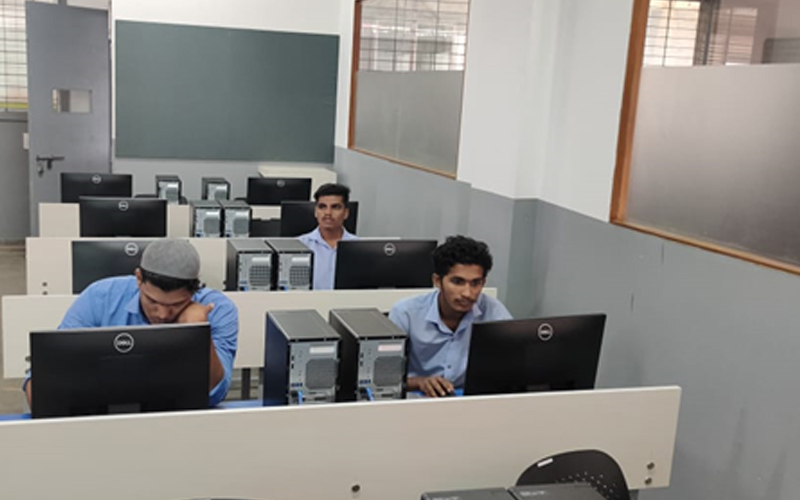



The CADD Laboratory is a central facility of the institute where all undergraduate and postgraduate students, research scholars and faculty members can work with the sophisticated 2-D & 3-D design and analysis software i.e Autocadd, StAAD-Pro, Primavera, Solid Edge, and 3DS-Max.
8. Environmental Engineering Laboratory
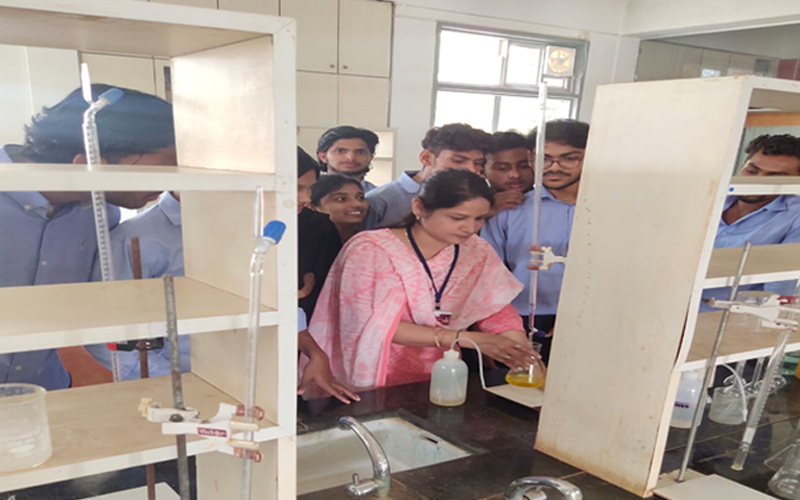
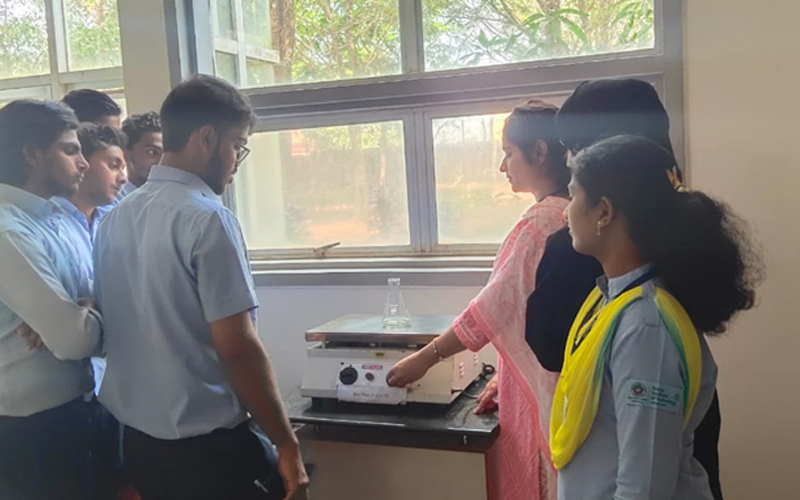
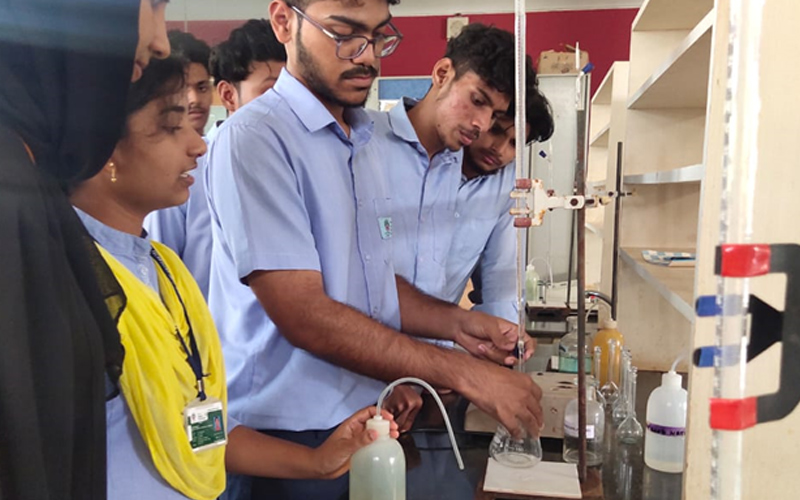



An Environmental Engineering Laboratory is a facility that tests various environmental samples to evaluate their quality and potential impact on human health and the environment. It performs water quality analysis, air quality monitoring, soil testing, and evaluates environmental remediation techniques for pollution control and waste management. The laboratory provides critical information for designing effective solutions for protecting human health and the environment.
EVENTS
Hands-on Workshop on Modern Surveying Using Total Station
The Department of Civil Engineering, Bearys Institute of Technology, Mangalore, successfully conducted a Hands-on Workshop on “Modern Surveying Using Total Station” on 8th January 2026, led by the resource person Mr. Sajith Kumar K, Senior Grade Lecturer, Vivekananda Polytechnic College. The workshop was structured in three progressive stages to ensure comprehensive learning and practical exposure for the student participants.
Bridging Engineering Education with Social Responsibility: Civil Engineering Students’ Outreach Visit to MCC Waste Management Plant
The Department of Civil Engineering, Bearys Institute of Technology, Mangaluru, corganized a...
Experiential Learning through Heritage and Social Responsibility: Civil Engineering Students’ Visit to Pilikula
The Department of Civil Engineering, Bearys Institute of Technology, Mangaluru, organized an...
Department of Civil Engineering Hosts “Food Walk” to Promote Social Responsibility and Cultural Awareness
The Department of Civil Engineering successfully organized a “Food Walk” on December 23, 2025, as part of its Social Connect and Responsibility (SCR) initiative at Bearys Institute of Technology. The event, held within the Civil Engineering Department, served as an innovative and educational exhibition celebrating India’s rich culinary diversity.
Achievement at NITTE Young Innovators Summit 2025
Team Ahraz, Ashwid, and Nooman presented their project “Sustainable Alkali-Activated Insulating Walling Material” at the NITTE Young Innovators Summit 2025 in association with K-Tech.
Khelotsav-25 Successfully Organised at Bearys Institute of Technology, Mangalore
The Department of Civil Engineering, in association with the Department of Physical Education and Sports, organised Khelotsav-25 on 1 and 2 December 2025 at the Bearys Arena. The event brought together students for two days of energetic and competitive sports activities.
BIT Civil Engineering Department Participated in the Tier-III Training Session on Aquifer Mapping and Groundwater Management Conducted by CGWB
The Civil Engineering final-year students and four faculty members from Bearys Institute of Technology successfully completed the Tier-III Training Programme on Aquifer Mapping, Groundwater-related Issues, and Groundwater Management.
Inaugural Ceremony of the Association of Civil Engineering (ACE 2025–26)
The Department of Civil Engineering at Bearys Institute of Technology, Mangalore organised the inaugural ceremony of the Association of Civil Engineering (ACE) for the academic year 2025–26. The event was held on 18 November 2025 at 9:30 AM in the Seminar Hall, in association with the IEEE GRSS Student Chapter.
Technical Talk on Machine Learning Models for Natural Disaster Prediction and Management
The Department of Civil Engineering at Bearys Institute of Technology, Mangalore organised a technical talk on the role of machine learning in natural disaster prediction and management. The event was held on 18 November 2025 in association with the IEEE GRSS Student Chapter, the Institution’s Innovation Council and the BIT IEEE Student Branch.
Inauguration of IEEE GRSS Student Branch Chapter and GRSS Lecture Series at Bearys Institute of Technology
The Departments of Civil, Electronics and Communication, and Computer Science Engineering of Bearys Institute of Technology (BIT), Mangalore, in association with IEEE, organized the Inauguration Ceremony of the IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society (GRSS) Student Branch Chapter along with the GRSS Lecture Series on 30th October 2025 at the International Seminar Hall.
Industrial Visit 2025: Exploring Sustainability, Heritage, and Innovation in Civil Engineering
The Department of Civil Engineering, Bearys Institute of Technology, Mangalore, organized a three-day Industrial Visit for the 2022 and 2023 batch students from 27th to 29th October 2025.The visit aimed to enhance students’ practical knowledge and provide exposure to real-world engineering applications.
World Green Building Week 2025 at Bearys Institute of Technology
Bearys Institute of Technology (BIT) and BIT Polytechnic jointly hosted the Inaugural Ceremony of World Green Building Week (WGBW) 2025 on 9th September 2025 at the International Seminar Hall, with enthusiastic participation from students of BIT, BIT Polytechnic, BEADS, BITPT, BIES, and BIPUC.
World Environment Day 2025 – Successfully Conducted at BIT Mangalore
Bearys Institute of Technology, Mangaluru, proudly organized World Environment Day 2025 on 14th June at 12:00 PM in the International Seminar Hall. The event, themed “Ending Global Plastic Pollution”, was jointly hosted by the Department of Civil Engineering and the Department of Basic Science, in association with IQAC and IIC.
Farewell Party for the Batch of 2021–2025
The Department of Civil Engineering, Bearys Institute of Technology, organised a warm and memorable Farewell Party for the outgoing Batch of 2021–2025. The event was hosted by the Association of Civil Engineering on 28 May 2025 at 11.00 am.
Exploring Opportunities After Civil Engineering with Industry Insights
The Department of Civil Engineering at Bearys Institute of Technology, Inoli, Mangaluru, in association with IQAC and Institution’s Innovation Council (IIC), organized an insightful guest talk on 16th May 2025 at 09:30 AM in Venue: B004.
Bearys Institute of Technology Celebrates World Earth Day 2025 with Inspiring Talks
Bearys Institute of Technology (BIT), Mangalore, observed World Earth Day 2025 with an engaging programme held at the International Seminar Hall on April 28.
Three-Day Faculty Development Program -2025
A three-day Faculty Development Program (FDP) titled “Advancing Pedagogy and Professional Growth” was inaugurated on January 21, 2025,and concluded on 23rd January 2025 at the Bearys Institute of Technology (BIT), Mangalore.
Three-Day Faculty Development Program on Advancing Pedagogy and Professional Growth Begins
The Department of Civil Engineering, Computer Science and Engineering, and Electronics and Communication Engineering at Bearys Institute of Technology (BIT), Mangalore, inaugurated a three-day Faculty Development Program (FDP) titled “Advancing Pedagogy and Professional Growth” on January 21, 2025.
Industry-Ready Engineers: Skills the Tech World is Hiring For
Bearys Institute of Technology, under the banner of BIT IEEE Student Branch, organized an engaging and informative session titled “Industry-Ready Engineers: Skills the Tech World is Hiring For” at the International Seminar Hall.
Beach Cleaning by NSS Unit of BIT – 2024
On Sunday, December 15, 2024, the NSS unit of Bearys Institute of Technology (BIT), organised a Beach cleaning drive at Ullal Beach with the theme “Clean Beach and Green Beach.”
ACHIEVEMENT
KSCST
| Year | Project Title | Group | Guide |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017-18 | Experimental Study on Effect of Replacement of Natural Sand by Manufactured Sand on the Properties of the Concrete | Mr. Naseer Ulla & Team | Prof. Altamashuddin Khan & Prof Akshatha |
| 2018-19 | Design of Sewage Treatment Plant for the Treatment of Hostel Waste Water at Bearys Institute of Technology | Mr Poomesh & Team | Prof. Shobhan Majumdar |
| 2019-20 | Assesment of Green Bearys Arena by 6D Building Information Modeling with Conventional Method | Mr Noman Ashraf and Team | Prof Zaheer Ahmed |
| 2020-21 | Partial Replacement of Coconut Shell and Demolished Building Waste as Coarse and Fine Aggregates in Construction - A Sustainable Approach | Mr. Kunhali raasik & Team | Prof. Deekshitha & Prof Zaheer Ahmed |
| 2021-22 | Machine Learning Model to Predict Compressive and Flexural Strength of Concrete Using M-Sand and PET Plastic Bottles as Fine Aggregates | Mr.Abdul Vahid & Team | Prof. Altamashuddin Khan |
| 2021-22 | Delineation of Ground Water Potential Zone of Mangalore Taluk using GIS & Remote Sensing | Mr Ahmed Shaqeeq & Team | Prof. Bharath Gowda |
| 2022-23 | Bearys Hostel Waste Water Treatment by Coconut Shell Activated Carbon and Laterite as a Low Cost Adsorbents | Miss Zulaika Haifa Afrin & Team | Prof Shareefa R Nadaf/ Prof. Bharath Gowda |
Dr. Pooja K
Publications
1. “Properties of Flyash- Dolomite Powder- Mangalore Tile Waste Powder Based Alkali-Activated Binder Cured in Ambient Condition”. Emergent Materials, 2024. (Q2)
2. “Bond Strength of Alkali-Activated Flyash Based Masonry System for Sustainable Construction”. SN Applied Science. 5, 360, 2023. DOI 10.1007/s42452-023-05555-w. (Q1)
3. ”Use of Individual Sized Aggregates in Manufacture of Alkali Activated Flyash Masonry Units”, ‘Masonry International’, Vol 34, No 3, 2023 (Q3).
4. “Recent Advances in Construction of Masonry Structure by Waste Materials”. ‘Sustainability Trends and Challenges in Civil Engineering, Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering’, Vol 162, PP 861–878, Springer, Singapore, 2022. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-16-2826-9_54. (Q4)
5. “Useful Application of Plastic Waste in Composite Brick Manufacturing” ‘Sahyadri International Journal of Research (SJIR), Vol 4, Issue 1, 2018.
6. “A Study on Heating and Cooling Regimes of Concrete at Elevated Temperature under Different Duration of Exposure” International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), Vol 5, Issue 6, 2018.
Patents
1. Indian Patent “A sustainable alkali activated ternary binder composite for masonry and a method of preparation thereof”.
2. Indian Patent “Composition and method for enhancing structural stability of masonry construction”.
3. Indian Patent “System and method for conversion of sunburnt bricks into second class bricks”.
Conference and Presentations
• “Investigation into the Utilization of Non-Disposable Boiler Slag as replacement for coarse aggregates in concrete” International conference on’ New Horizons in Civil Engineering (NHCE-2023)’ held during 13th and 14th October, 2023, organized by the department of civil engineering, MIT Manipal.
• “Development of Sustainable Alkali Activated Masonry Blocks from Industrial Wastes” Poster presentation in New Horizons in Civil Engineering (NHCE-2023)’ held during 13th and 14th October, 2023, organized by the department of civil engineering, MIT Manipal.
• “Tailoring Alkali Activated Flyash Binders with Dolomite Powder for Enhanced Performance of Masonry Units”, 2nd International conference on ‘Innovations in Mechanical and Civil Engineering (i-MACE-2023)’ held during 18th and 19th of August 2023 organized by the department of civil and mechanical engineering, Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering, Pune, Maharashtra.
• “Effective Utilization of Dolomite Powder in Alkali Activated Flyash Based Masonry Units” conference on ‘Sustainable Infrastructure: Innovation, Opportunities and Challenges’ (SIIOC 2023)’ held during 20th and 21st April 2023 organized by the department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology (NITK) Surathkal, Karnataka.
• “An Experimental Study on the Production of Alkali Activated Flyash Solid and Hollow Blocks”, ‘Manipal Research Colloquium’ held at Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal held from 12th to 14th April 2023.
• “Recent Advances in Construction of Masonry Structure by Waste Materials” ‘International Conference on Civil Engineering Trends and Challenges for Sustainability’ (CTCS 2020) conference held during 22nd and 23rd, 2020 organized by the Department of Civil Engineering, N.M.A.M. Institute of Technology, Nitte, Karkala, Karnataka.
• “Contour Crafting Technology”, PRASTUTI- a National Level Technical Paper Presentation held on May 5th during TECHZONE- 2017 organized at JNN college of Engineering Shivamogga, Karnataka.
Aleema Safa
- Development of arduino prototype for the detection of fire, smoke and carbon monoxide from open waste burning
- Surface water quality assessment using sentinel – 2: A case study of the Netravati – Gurupura estuary, Karnataka, India
Dr. Nalini E Rebello
1. Rebello, N., Harikiran, R., Akarsh, Vasani, S. & Aseem, S. Experimental Studies on Geo-Synthetic Vertical Barrier Around the Dumpyard. in Trends in Civil Engineering and Challenges for Sustainability (eds. Narasimhan, M. C., George, V., Udayakumar, G. & Kumar, A.) 603–610 (Springer Singapore, 2021).
2. Deekshitha, K. et al. A novel cross-linked PVA-Chitosan composite membrane for heavy metal filtration applications. Mater. Today Proc. 66, 2493–2498 (2022).
3. Shivashankar, R., Rebello, N. E., Sastry, V. R. & Jayalekshmi, B. R. Soil Structure Interaction Studies with Use of Geosynthetics in Soils Beneath Footings. in Numerical Analysis of Nonlinear Coupled Problems (eds. Shehata, H. & Rashed, Y.) 85–97 (Springer International Publishing, 2018).
4. Rebello, N., Safa, A., Pujar, A. Y., Joseph, B. & Deekshith, V. C. Development of Arduino Prototype for the Detection of Fire, Smoke, and Carbon Monoxide from Open Waste Burning. in Recent Advances in Civil Engineering (eds. Nandagiri, L., Narasimhan, M. C. & Marathe, S.) 967–975 (Springer Nature Singapore, 2023).
5. Deekshitha, K., Rebello, N., Ramaprasad, A. T., Jayarama, A. & Pinto, R. Development of novel porous membrane for filtration of dump yard ground water contaminants. Mater. Today Proc. 35, 405–408 (2021).
6. Rebello, N., Rao, M. S., D’Souza, M. R., Mahesha, S. M. & Rajeev, V. T. Development of Water Filtration Unit Using PVA-Based Composite Membrane and Fly Ash. in Trends in Civil Engineering and Challenges for Sustainability (eds. Narasimhan, M. C., George, V., Udayakumar, G. & Kumar, A.) 611–618 (Springer Singapore, 2021).
Prof. Purushothama. C. T
1. Purushothama C.T, Badruddin P.M, Harshith S Poonja, Kalandar Shafee, Shakeel Ahmed, Mohammed Maqsood, “Comparative Study on Compressive Strength and Splitting Tensile strength of Fiber reinforced concrete and Conventional concrete”, International Journal of Novel Research and Development, Vol 8, June 2023, pp 625-631.
2. Purushothama C.T, I.R. Mithanthaya, “Comparative Study on Strength of Partial RCC Beam by Experimental results and ANSYS Software results”, Industrial Engineering Journal, Vol 15, December 2022, pp 478-490.
3. Purushothama C.T, I.R. Mithanthaya, “Impact of Hybrid fibers on Properties of Fresh concrete and strength of Hardened concrete”, Advanced Engineering Science Journal, Vol 54, December 2022, pp 6213-6223.
4. Purushothama C.T, I.R. Mithanthaya, “Comparative Study of Conventional and Partial RCC Beams and Slabs for Flexural and Shear strength”, Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education, Vol 12, April 2021, pp 126-128.
5. Purushothama C.T, Harshith H.J, “Stiffening of Earthquake Resistant Green Buildings”, Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research, Vol 6, May2019, pp 35-39.
6. Purushothama C.T, I.R. Mithanthaya, “Architectural problems in earthquake resistant buildings”, International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Vol 7, June 2016, pp 522-528.
7. Paper presentation – 8 th International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering (ICETE2018) – NMAMIT, Nitte. Purushothama C.T, Chandana V.V, I.R.Mithanthaya “Finite Element Analysis of Concrete Filled Steel Tubes Subjected to Axial Compression”
Prof. Zaheer Ahmed
- Zaheer Ahmed. Assessement of Green Bearys Arena by 6D Building Information Modeling Compared with Conventional Method review (2020)
Dr. Altamashuddin Khan Nadeemallah
PUBLICATIONS
1. Machine Learning Models for Predicting the Compressive Strength of Concrete with Shredded PET Bottles and M-Sand as Fine Aggregate – Scopus & Web of Science – 2025
2. The Relation Between Destructive and Non-destructive Test of Concrete Incorporated with Dredged Sediment as Fine Aggregate Replacement – Scopus – 2024
3. Effect of Exfoliated Vermiculite as Fine Aggregate Replacement on Properties of Lightweight Concrete – 2023
4. Machine Learning Model to Predict Slump, VEBE and Compaction Factor of M Sand and Shredded PET Bottles Concrete – 2022
5. Correlation Between Slump, VeBe and Compaction Factor of Concrete Containing Shredded PET Bottles, Manufactured Sand (M-sand) and River Sand as Fine Aggregate – 2021
6. The Relation of Compression Strength with Modulus of Rupture and UPV of Concrete Containing M-sand as Fine Aggregate – Scopus– 2020
7. The Impact of Manufactured Sand (M-Sand) as Partially and Fully Replacement of Fine Aggregate in Concrete – Scopus– 2020
8. The Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Bottles Waste as a Fine Aggregate Replacement in Concrete –– 2020
9. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Bottles Waste as Fine Aggregate in Concrete – Scopus – 2019
10. The Effect of Replacement of Natural Sand by Manufactured Sand on the Properties of the Concrete – Scopus & Web of Science – 2018
CONFERENCES
1. “The Effect of Replacement of Natural Sand by Manufactured Sand on the Properties of the Concrete”, paper presented at 2018 IEEE 5th International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Applied Sciences (ICETAS), November 22-23, 2018, Bangkok Thailand.
2. “Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Bottles Waste as Fine Aggregate in concrete-A Review” , paper presented at SURF-2019, April 26-27, Mangalore, Karnataka, India.
3. “The Effect Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Bottles Waste as a Fine Aggregate Replacement in Concrete”, paper presented at 4th International Conference on Advances in Manufacturing and Materials Engineering 2019, October 30 – 31, Putrajaya International Convention Centre (PICC) Putrajaya.
4. “Correlation Between Slump, VeBe and Compaction Factor of Concrete Containing Shredded PET Bottles, Manufactured Sand (Msand) and River Sand as Fine Aggregate”, paper presented at 5th International Conference on Advanced Technology and Applied Sciences (ICATAS 2020) in Conjunction with Malaysia-Japan Joint International Conference (MJJIC 2020) 7-9th October 2020, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
5. “Machine Learning Model to Predict Slump, VEBE and Compaction Factor of M Sand and Shredded Pet Bottles Concrete”, Paper presented at 5th International Conference on Mechanical, Automotive and Aerospace Engineering (ICMAAE 2021) 22nd and 23rd June 2021 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
6. “Air Quality Index Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques: A Data-Driven Approach for Environmental Monitoring”, PACE Conclave 2024 (International Conclave On Engineering Sciences And Technology-23, 24th April 2024)
HONOURS AND AWARDS
1. GOLD AWARD (KERICE- 2020)
Kulliyyah of Engineering Research, Innovation and Commercialization Exhibition (KERICE) 2020, organized by Kulliyyah of Engineering, International Islamic University Malaysia.
2. BRONZE AWARD (KERICE- 2019)
Kulliyyah of Engineering Research, Innovation and Commercialization Exhibition (KERICE) 2019, organized by Kulliyyah of Engineering, International Islamic University Malaysia.
3. YOUNG SCIENTIST AWARD
International Scientist Awards on Engineering, Science and Medicine, held on 28 & 29- Aug-2021, Trivandrum, India, Organized by VDGOOD Professional Association.
BOOKS PUBLISHED
1. Analysis and Design of Steel Trusses by Post-Tensioning Method Using Sap2000v15
LAP Lambert Academic Publishing (published on 17 January 2013) ISBN: 9783659317743, 3659317748.
2. Manufactured Sand as Fine Aggregate in Concrete
Eliva Press (published on April 16, 2021), ISBN-10: 1636481671, ISBN-13: 978-1636481678.
3. Smart Solutions for Civil Engineering Using Machine Learning
Notion Press (2 December 2024), ISBN-13 : 979-8896322665
4. Machine Learning Applications in Concrete Strength Prediction
LAP Lambert Academic Publishing (November 19, 2024), ISBN-10 : 3659949310
ISBN-13 : 978-3659949319
Mr. Badruddin P M
1. Mohd Minhajuddin, Altamashuddinkhan Nadimalla, Badruddin P M, A. R. P. (2023). Effect of Exfoliated Vermiculite as Fine Aggregate Replacement on Properties of Lightweight Concrete. International Journal of Novel Research and Development, 8(5 May 2023), 309–311.
2. Purushothama C.T, Badruddin P.M, Harshith S Poonja, Kalandar Shafee, Shakeel Ahmed, Mohammed Maqsood, “Comparative Study on Compressive Strength and Splitting Tensile strength of Fiber reinforced concrete and Conventional concrete”, Industrial Engineering Journal, Vol 8, June 2023, pp 625-631.
Mohd Minhajuddin
1. Mohd Minhajuddin, Altamashuddinkhan Nadimalla, Badruddin P M, A. R. P. (2023). Effect of Exfoliated Vermiculite as Fine Aggregate Replacement on Properties of Lightweight Concrete. International Journal of Novel Research and Development, 8(5 May 2023), 309–311.
Prof. ANJAN KUMAR M.U
1. Journal publications:
Anjan Kumar M.U1, Dr.AshaUdaya Rao2 ,Dr.Narayan Sabhahith3 “Reactive Powder Concrete Properties with Cement Replacement Using Waste Material”, International journal of Scienticfic & Engineering Research, vol.4, issue 5, may, pp 203-206
2. Paper presentation- National Conference
Anjan Kumar M.U1, Dr. Asha Udaya Rao2 ,Dr.Narayan Sabhahith3, Reactive Powder Concrete With Mineral Admixture, National Conference on New Horizons in Civil Engineering–NHCE 2013,Manipal Institute Of Technology, Manipal, April 12-13, 2013.
3. Paper presentation- International Conference
Mr.Anjankumar M U, Dr. Asha Udaya Rao, Dr. Narayana Sabhahit, Reactive Powder Concrete Properties with Cement Replacement Using Waste Material, International Conference On Innovations In Civil Engineering ICICE-2013, SCMS School of Engineering Technology, Karukutty, Kerala, India, 9th and 10thMay, 2013.
Prof. VIJAY H
1. Vijay H, “Reusing Treated Effluents for making concrete”, International Journal of Latest technology in engineering management & applied science, Vol 6, Issue I, Jan 2017, pp 21-29
2. Vijay H, T.N. Shridhara, “Effects of the physico-chemical characteristics of treated wastewater effluents on their reuse in plain concrete works, Apri 2014






















